alb5411402
Navigation, Sighting Compass,1768
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |



Haben Sie bereits ein Konto? Anmelden
Sie haben kein Konto? Registrieren
Dieses Bild kaufen.
Nutzung auswählen:

Titel:
Navigation, Sighting Compass,1768
Untertitel:
Siehe automatische Übersetzung
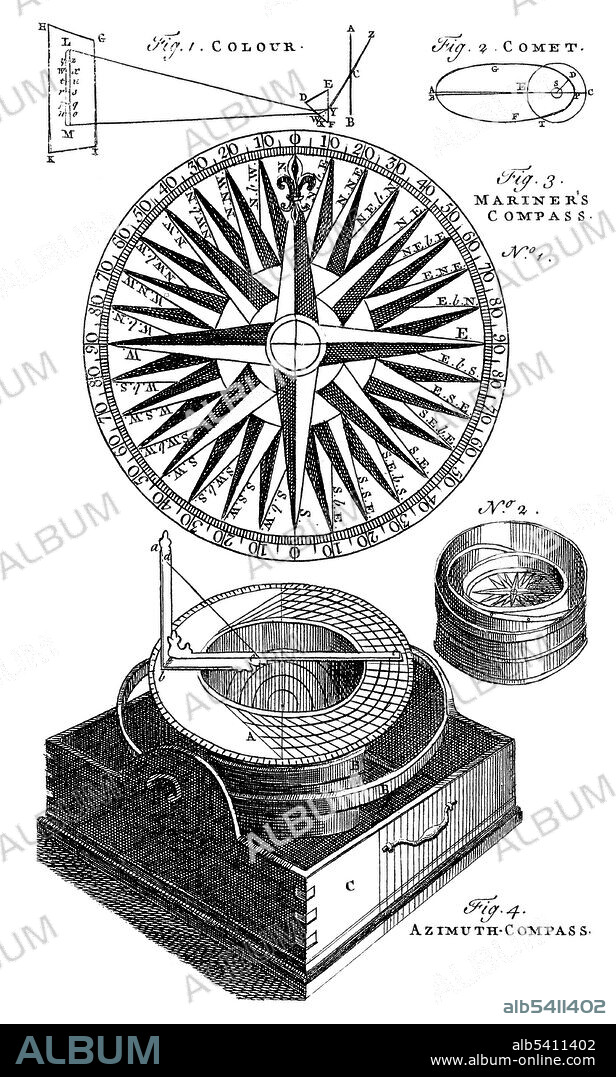
Navigation: a sighting compass. A hand compass (also hand bearing compass or sighting compass) is a compact magnetic compass capable of one-hand use and fitted with a sighting device to record a precise bearing or azimuth to a given target or to determine a location. A compass is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions (or points). Usually, a diagram called a compass rose shows the directions north, south, east, and west on the compass face as abbreviated initials. North corresponds to 0°, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90° degrees, south is 180°, and west is 270°. These numbers allow the compass to show azimuths or bearings, which are commonly stated in this notation. The first compasses in ancient Han dynasty China were made of lodestone, a naturally magnetized ore of iron. The compass was later used for navigation during the Song Dynasty of the 11th century. Later compasses were made of iron needles, magnetized by striking them with a lodestone. Dry compasses began to appear around 1300 in Medieval Europe and the Islamic world. No artist credited, 1768.
Bildnachweis:
Album / Science Source
Freigaben (Releases):
Model: Nein - Eigentum: Nein
Rechtefragen?
Rechtefragen?
Bildgröße:
2889 x 4800 px | 39.7 MB
Druckgröße:
24.5 x 40.6 cm | 9.6 x 16.0 in (300 dpi)
Schlüsselwörter:
18. JAHRHUNDERT • 18. JH. • ADRESSE • BERÜHMT • BERÜHMTE PERSÖNLICHKEIT • GEOGRAFIE • GEOGRAPHIE • NAVIGATION • PROMINENZ • RICHTUNGE
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Link kopieren
Link kopieren Email
Email
