alb3802562
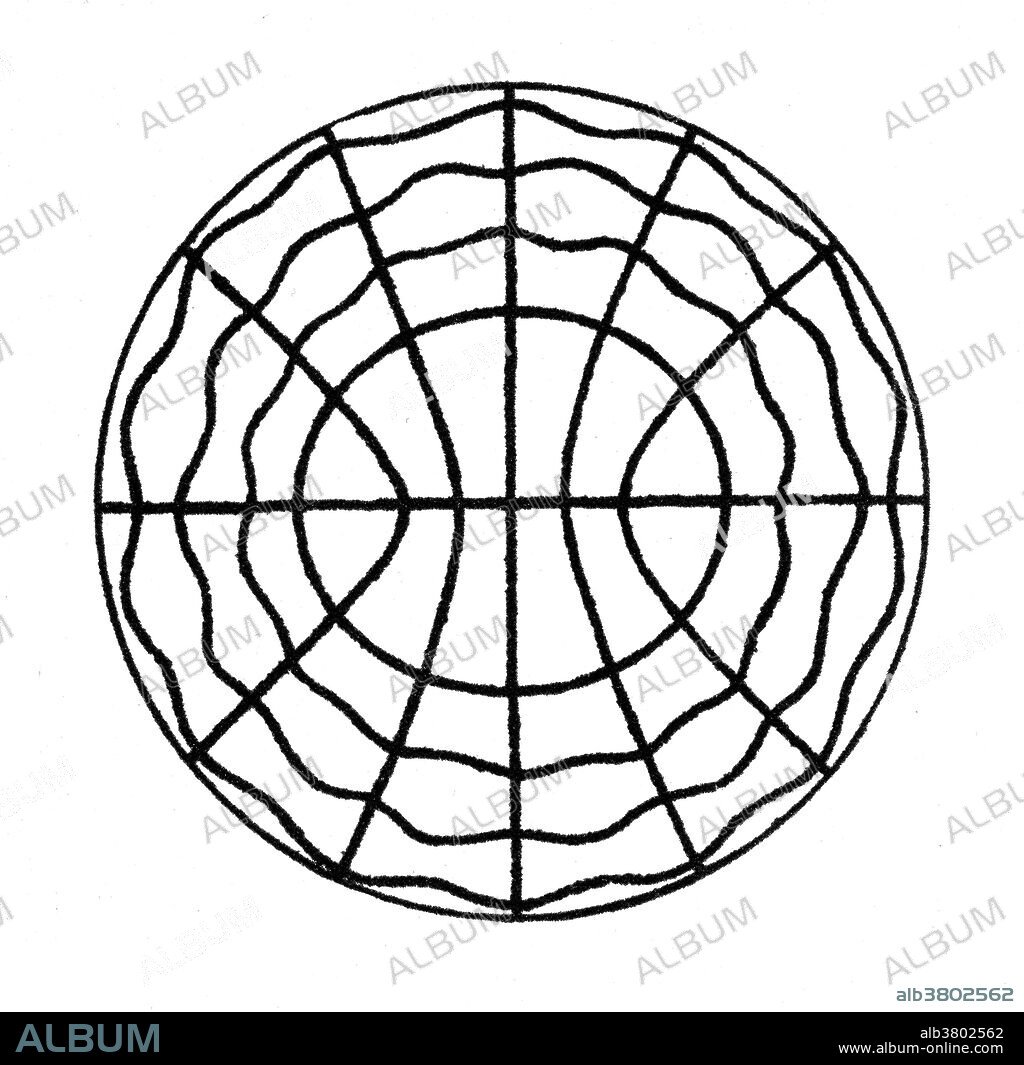
Acoustic Sound Waves, Ernst Chladni, 1787
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |



Haben Sie bereits ein Konto? Anmelden
Sie haben kein Konto? Registrieren
Dieses Bild kaufen.
Nutzung auswählen:

Titel:
Acoustic Sound Waves, Ernst Chladni, 1787
Untertitel:
Siehe automatische Übersetzung
Illustration of acoustic waves: the sound figures which Chladni created for his book, Discoveries About the Theory of Sound, 1787. Ernst Florens Friedrich Chladni (November 30, 1756 - April 3, 1827) was a German physicist and musician who is considered by many to be the "Father of Acoustics". He studied law and philosophy, and obtained a law degree in 1782 from the University of Leipzig. When his father died in 1782, Chladni began his research in physics. One of his most famous achievements was inventing a technique to show the various modes of vibration of a rigid surface. A plate or membrane vibrating at resonance is divided into regions vibrating in opposite directions. Chladni's technique consisted of drawing a bow over a piece of metal whose surface was lightly covered with sand. The plate was bowed until it reached resonance, when the vibration causes the sand to move and concentrate along the nodal lines where the surface is still, outlining the nodal lines. These patterns are now called Chladni figures.
Bildnachweis:
Album / Science Source / New York Public Library
Freigaben (Releases):
Model: Nein - Eigentum: Nein
Rechtefragen?
Rechtefragen?
Bildgröße:
3900 x 3855 px | 43.0 MB
Druckgröße:
33.0 x 32.6 cm | 13.0 x 12.9 in (300 dpi)
Schlüsselwörter:
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Link kopieren
Link kopieren Email
Email
