alb3794615
Lone Star Tick Nymph
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |
|
Zu einem anderen Lightbox hinzufügen |



Haben Sie bereits ein Konto? Anmelden
Sie haben kein Konto? Registrieren
Dieses Bild kaufen.
Nutzung auswählen:

Titel:
Lone Star Tick Nymph
Untertitel:
Siehe automatische Übersetzung
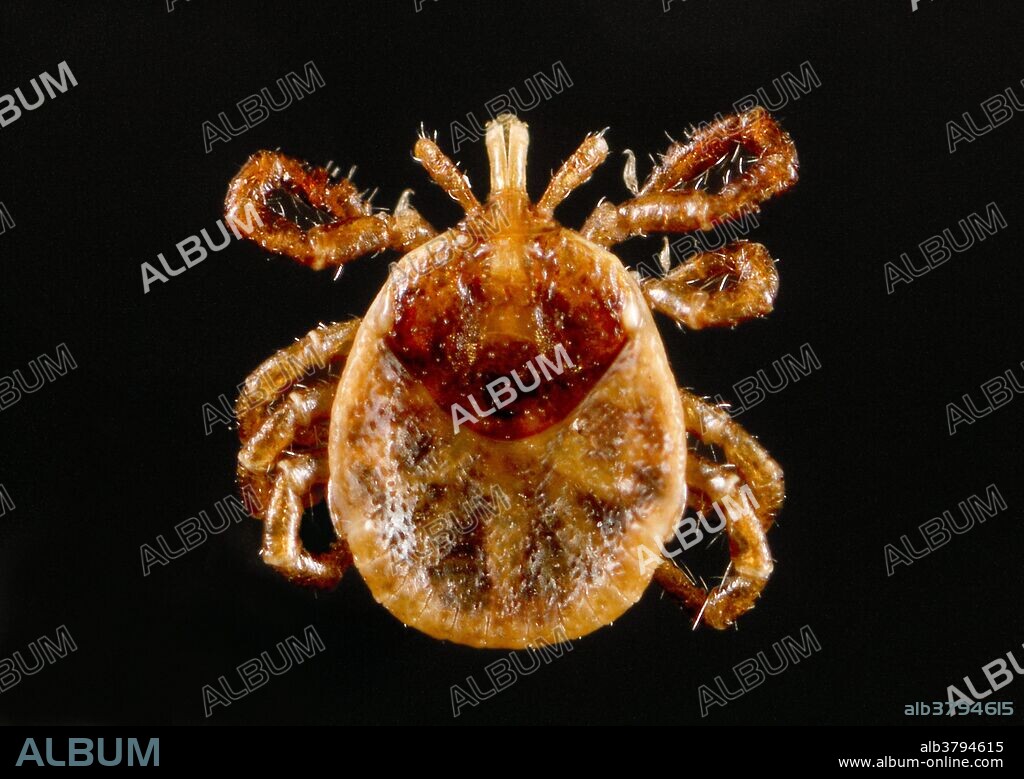
Dorsal view of an immature, or nymphal, "lone star tick", Amblyomma americanum. Nymphal ticks are much smaller than adult ticks, and people might not notice a nymph until it has been feeding for a few days. Nymphs are, therefore, more likely than adult ticks to transmit diseases to people. An Ixodes or "hard" tick, A. americanus is found through the southeast and south-central states, and has been shown to transmit the spirochete, Borrelia lonestari, the pathogen responsible for causing a Lyme disease-like rash known as "Southern tick-associated associated rash illness" (STARI). Representatives from all three of its life stages aggressively bite people in the southern U.S. Research indicates that live spirochetes are observed in only 1-3% of specimens. Persons who have been bitten by a lone star tick, A. americanum, and who develop a red, expanding rash with central clearing, known as "erythema migrans", headache or myalgia with fever, should see their physician.
Bildnachweis:
Album / Science Source / James Gathany/CDC
Freigaben (Releases):
Model: Nein - Eigentum: Nein
Rechtefragen?
Rechtefragen?
Bildgröße:
3595 x 2550 px | 26.2 MB
Druckgröße:
30.4 x 21.6 cm | 12.0 x 8.5 in (300 dpi)
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Link kopieren
Link kopieren Email
Email
