alb3844093
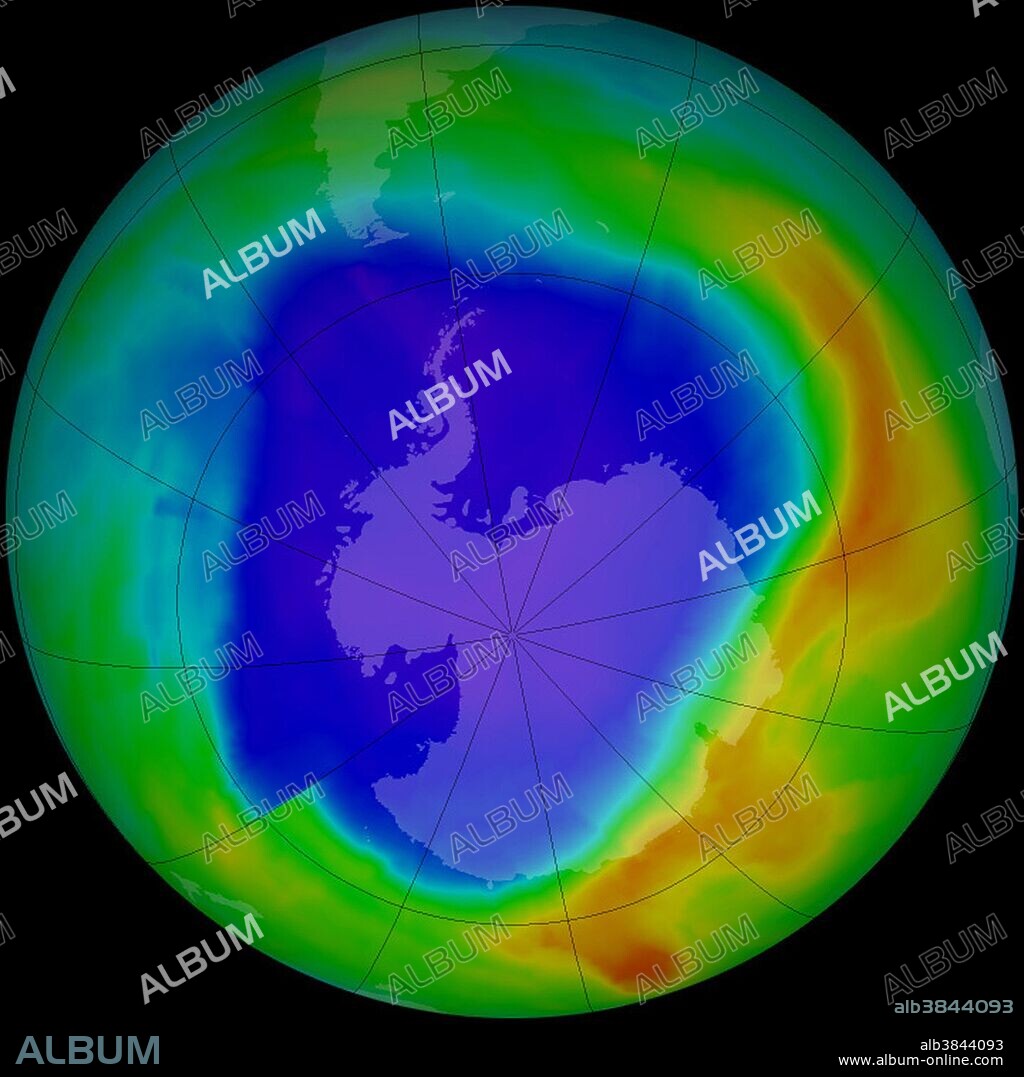
Antarctic Ozone Hole, 2013
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Buy this image.
Select the use:

Title:
Antarctic Ozone Hole, 2013
Caption:
The ozone hole over Antarctica was slightly smaller in 2013 than the average for recent decades, according to data from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA's Aura satellite and the Ozone Monitoring and Profiler Suite (OMPS) on the NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite. The average size of the hole in September/October 2013 was 21.0 million square kilometers (8.1 million square miles). The average size since the mid 1990s is 22.5 million square kilometers (8.7 million square miles). This image shows ozone concentrations over the South Pole on September 16, 2013, as measured by OMI. The ozone hole is a seasonal phenomenon that starts during the Antarctic spring (August and September) as the sun begins rising after winter darkness. Pole-circling winds keep cold air trapped above the continent, and sunlight catalyzes reactions between ice clouds and chlorine compounds that begin eating away at natural ozone in the stratosphere. In most years, the conditions for ozone depletion ease by early December, when the seasonal hole closes.
Credit:
Album / Science Source / NASA Ozone Watch
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
2835 x 2835 px | 23.0 MB
Print size:
24.0 x 24.0 cm | 9.4 x 9.4 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
ANTARCTIC • ANTARCTICA • CARBON EMISSIONS • CLIMATE CHANGE • CLIMATE • COMPUTER MODEL • DATA VISUALIZATION • DATA • DIAGRAM • EARTH FROM ABOVE • ECOLOGY • ENVIRONMENT • GLOBAL WARMING • GLOBE • HOLE IN OZONE LAYER • IMAGING • MODEL • OZONE DEPLETION • OZONE HOLE • OZONE LAYER • OZONE • SATELLITE IMAGE • SATELLITE VIEW • SCIENCE • VISUALIZATION
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email
