alb3769850
Mast Cell
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Title:
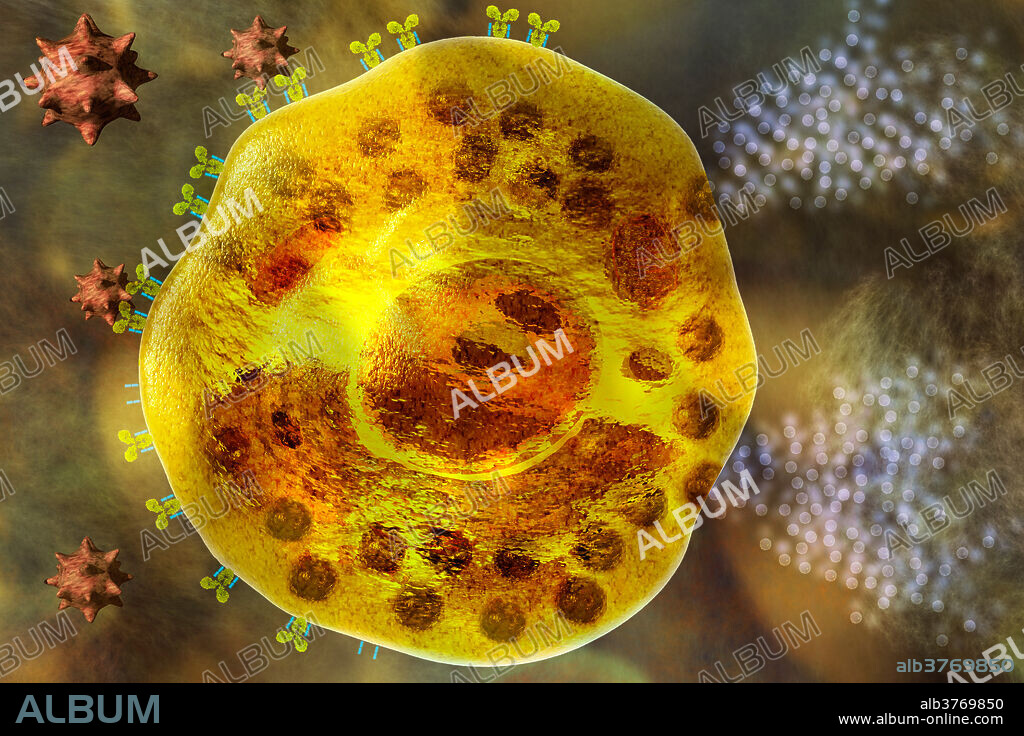
Mast Cell
Caption:
Mast cell. This leukocyte (white blood cell) contains the chemical mediators histamine, serotonin and heparin, held in granules (brown spheres) in its cytoplasm. Mast cells are part of the immune system; they release their contents during a localized inflammatory immune response to invading pathogens, and during an allergic reaction, as shown here. The allergen cross bonds with two Immunoglobulin antibodies on the cell surface, triggering the granules to discharge their contents. Histamine and serotonin cause the symptoms of allergies. Heparin is an anticoagulant that may prevent the formation of blood clots between the body's cells.
Credit:
Album / Science Source / Carol and Mike Werner
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
6060 x 4040 px | 70.0 MB
Print size:
51.3 x 34.2 cm | 20.2 x 13.5 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
ACID • ALLERGEN • ALLERGIES • ALLERGY • ANSWER • ARACHIDONIC • CELL • CHEMOTACTIC • CYTOKINE • FACTOR • HISTAMINE • HUMAN • HUMANE • ILLUSTRATION • ILLUSTRATIONS • IMMUNE • INDIVIDUAL • MAIL • MAST • MATT • MEDICAL • MEDICINAL • METABOLITE • PERSON • POLE • POST • PROTEASE • RESPONSE • SCIENCE • SYSTEM
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email

