alb3798159
HIV-1, Human Immunodeficiency Virus, SEM
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Buy this image.
Select the use:

Title:
HIV-1, Human Immunodeficiency Virus, SEM
Caption:
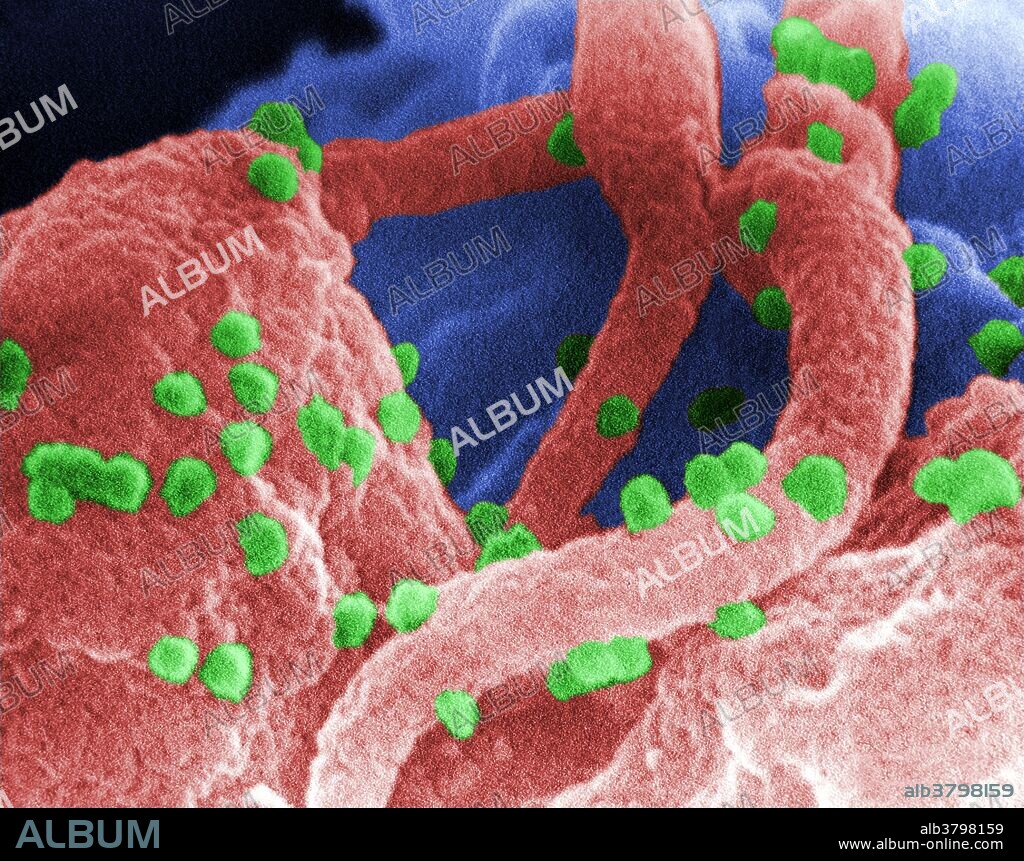
Scanning electron micrograph revealed the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1), (spherical in appearance), which had been co-cultivated with human lymphocytes. Note the lymphocyte in the lower left, and some of its extended pseudopodia. HIV-1 virions can be seen on the surface of this lymphocyte. A retrovirus, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) was identified in 1983 as the pathogen responsible for the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). AIDS is characterized by changes in the population of T-cell lymphocytes that play a key role in the immune defense system. In the infected individual, the virus causes a depletion of T-cells, called T-helper cells, which leaves these patients susceptible to opportunistic infections, and certain malignancies.
Category:
Microbiology: Virus
Credit:
Album / CDC/Science Source
Releases:
Image size:
4200 x 3314 px | 39.8 MB
Print size:
35.6 x 28.1 cm | 14.0 x 11.0 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
ABNORMAL • ACQUIRED IMMUNE DEFICIENCY SYNDROME • AIDS • AUTO-IMMUNE DEFICIENCY SYNDROME • CAUSATIVE AGENT • COLORIZED • COMMUNICABLE DISEASE • DISEASED • ELECTRON MICROGRAPH • ELECTRON MICROSCOPY • EM • ENHANCEMENT • HISTOPATHOLOGICAL • HISTOPATHOLOGY • HIV / AIDS • HIV • HIV-1 • HIV1 • HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS • IMMUNE DEFICIENCY • IMMUNE SYSTEM • IMMUNOLOGY • INFECTIOUS DISEASE • LENTIVIRUS • LYMPHOCYTE • MEDICAL • MEDICINAL • MICROBIOLOGY • MICROBIOLOGY: VIRUS • MICROGRAPH • MICROORGANISM • MICROSCOPIC ORGANISM • MICROSCOPIC • MICROSCOPY • PATHOGEN • PATHOGENIC • PATHOLOGICAL • PATHOLOGY • RETROVIRUS • SCANNING ELECTRON MICROGRAPH • SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE • SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY • SCIENCE • SEM • SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASE • STD • TRANSMISSIBLE DISEASE • UNHEALTHY • VENEREAL DISEASE • VIRAL DISEASE • VIRAL • VIRION • VIROLOGY • VIRUS PARTICLES • VIRUS • WBC • WHITE BLOOD CELL • WHITE CELL
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email
