alb3823404
Libra Constellation, Zodiac Sign, 1825
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Buy this image.
Select the use:

Title:
Libra Constellation, Zodiac Sign, 1825
Caption:
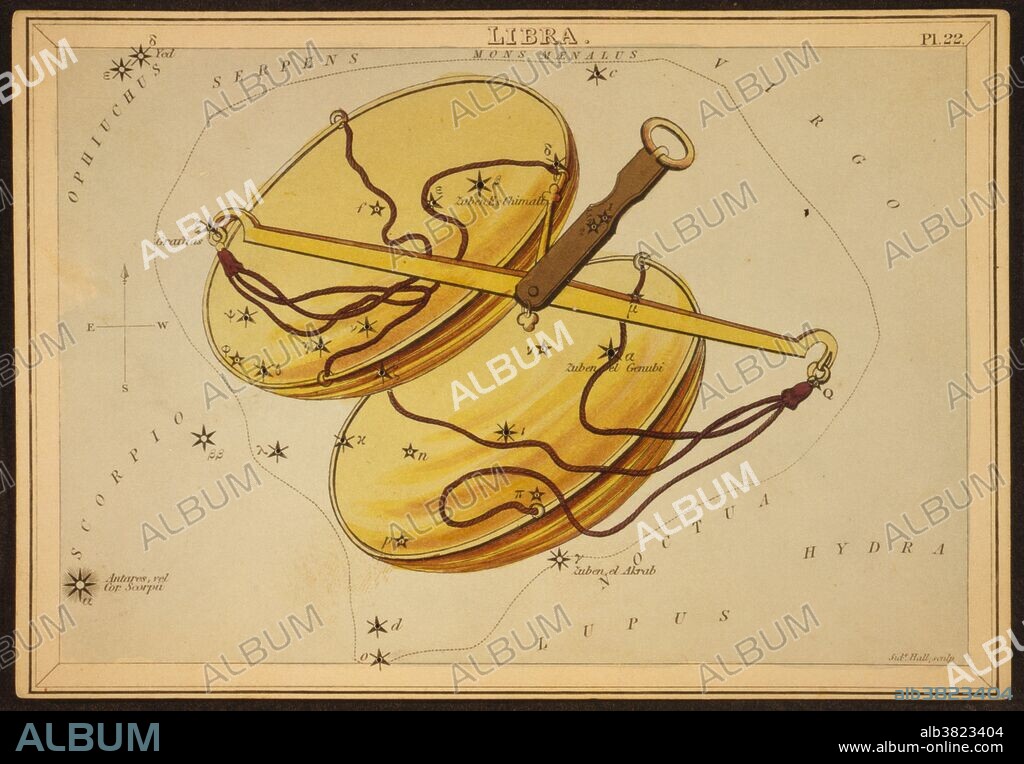
Astronomical chart showing a balance forming the constellation. Libra constellation. Ptolemy's Star Catalogue, from a late Latin version of the Almagest, 1490. Libra is a constellation of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for weighing scales. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. Libra is a constellation not mentioned by Eudoxus or Aratus. In Roman mythology, Libra is considered to depict the scales held by Astraea (identified as Virgo), the goddess of justice. Libra was known in Babylonian astronomy as MUL Zibanu (the scales). The scales were held sacred to the sun god Shamash, who was also the patron of truth and justice. Libra has been associated with law, fairness and civility. Libra is the seventh astrological sign of the zodiac, originating from the constellation of Libra. It spans the 180-210th degree of the zodiac, between 180 and 207.25 degree of celestial longitude, which the Sun transits this area on average between September 23 to October 22 each year. Urania's Mirror is a boxed set of 32 constellation cards first published by Samuel Leigh of the Strand, London, in or shortly before 1825. An unidentified lady, referred to by her nom-de-plume, Jehoshaphat Aspin, designed these whimsical astronomy cards. The engraver was Sidney Hall.
Credit:
Album / LOC/Science Source
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
3889 x 2700 px | 30.0 MB
Print size:
32.9 x 22.9 cm | 13.0 x 9.0 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
1825 • 19TH CENTURY • ART • ARTWORK • ASPIN • ASTERISM • ASTROLOGICAL • ASTROLOGY • ASTRONOMIA • ASTRONOMICAL • ASTRONOMY CARD • ASTRONOMY • CELEBRITIES • CELEBRITY • CELESTIAL BODY • CELESTIAL SPHERE • CELESTIAL • CONSTELLATION CARD • CONSTELLATION • DRAWING • ENGRAVING • FAMOUS PEOPLE • FAMOUS • HEAVENLY BODY • HEAVENLY • HISTORIC • HISTORICAL • HISTORY • HOROSCOPE • ILLUSTRATION • ILLUSTRATIONS • IMPORTANT • JEHOSHAPHAT ASPIN • LIBRA • NOTABLE • OCCULT • OCCULTISM • PATTERN OF STARS • SCALES, THE • SCIENCE • SIDNEY HALL • SIGNS OF THE ZODIAC • SIGNS • STAR CHART • STAR MAP • URANIA'S MIRROR • WELL-KNOWN • ZODIAC • ZODIACAL
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email
