alb10666004
Normal Brain vs. Alzheimer's Disease, MRI Scan
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Buy this image.
Select the use:

Title:
Normal Brain vs. Alzheimer's Disease, MRI Scan
Caption:
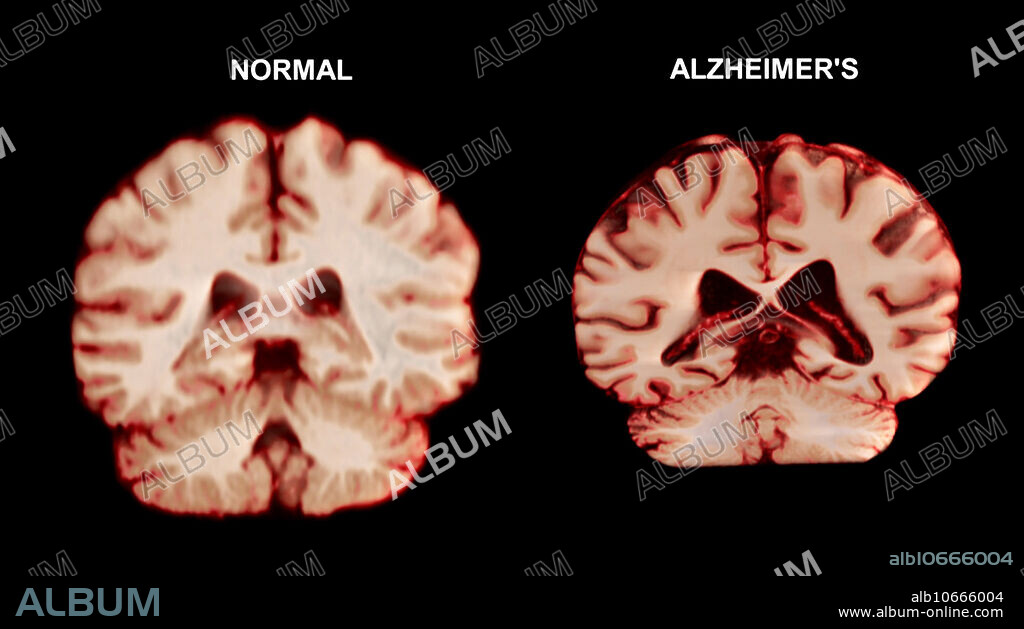
Visualization comparing a normal brain and a brain affected by Alzheimer's disease. The brain affected by Alzheimer's is considerably shrunken, due to the degeneration and death of nerve cells. Apart from a decrease in brain volume, the surface of the brain is often more deeply folded. Tangled protein filaments (neurofibrillary tangles) occur within nerve cells, and patients also develop brain lesions of beta-amyloid protein. Alzheimer's disease accounts for most cases of senile dementia. Symptoms include memory loss, disorientation, personality change and delusion.
Credit:
Album / Science Source / Anatomical Travelogue
Releases:
Image size:
3556 x 2000 px | 20.3 MB
Print size:
30.1 x 16.9 cm | 11.9 x 6.7 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
ABNORMAL • ALZHEIMERS • ANATOMICAL • ANATOMY • BAD STORM • BALANCE • BRAIN • CALLOSUM • CENTRAL • CEREBELLUM • CEREBRAL • CEREBRI • CEREBRO • CEREBRUM • CHRONIC • CNS • COGNITION • COGNITIVE • COMPARE • COMPARING • COMPARISON • CONDITION • CORONAL • CORPUS • CORTEX • CROSS CUT • CROSS • CROSS-CUT • CROSS-SECTION • CROSS-SECTIONED • CUT • DATA • DISEASE • DISEASED • DISORDER • FORNIX • GRAY • GREY • GROSS ANATOMY • HEALTHCARE • HEALTHY • HUMAN • HUMANE • ILLNESS • IMAGING • INDIVIDUAL • LATÉRAL • LATERALIS • LOBE • LOBULE • MAGNETIC • MALADY • MATTER • MEDICAL • MEDICINAL • MEDICINE • MESS • MESSY • METEOROLOGICAL_DISASTER • MRI • NERVOUS • NEURODEGENERATIVE • NEURONORMAL • NORMAL • ORGAN • PATHOLOGICAL • PATHOLOGY • PERSON • PHYSIOLOGICAL • PHYSIOLOGIE • PHYSIOLOGY • REGION • RESONANCE • SCANNED • SECTION • SECTIONAL • SECTIONED • SEVERE STORM • SICKNESS • SIDE • SKILLS • SONORITY • STORM • STORMS • SYSTEM • TEMPEST • TEMPORAL • TEMPORARY • THALAMUS • THIRD • THUNDERSTORM • UNHEALTHY • VENTRICLE • VIEW • WEATHER: STORM • WEATHER: THUNDERSTORM • WHITE
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email
