alb9204324
PHA's, Potentially Hazardous Asteroids
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Title:
PHA's, Potentially Hazardous Asteroids
Caption:
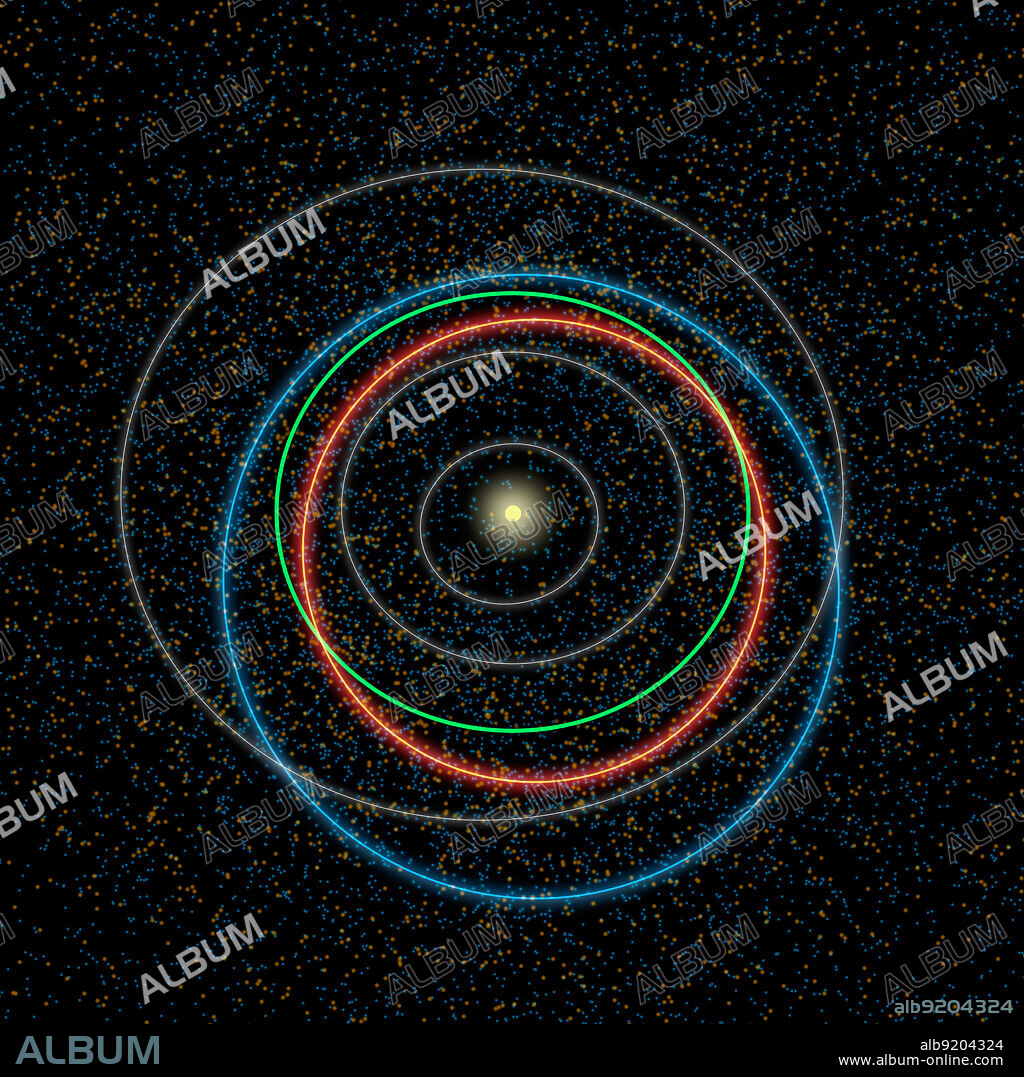
This diagram illustrates the differences between orbits of a typical near-Earth asteroid (blue) and a potentially hazardous asteroid, or PHA (orange). PHAs are a subset of the near-Earth asteroids (NEAs). They have the closest orbits to Earth's orbit, coming within 5 million miles (about 8 million kilometers), and they are large enough to survive passage through Earth's atmosphere and cause damage on a regional, or greater, scale. Our yellow sun sits at the center of the crowd, while the orbits of the planets Mercury, Venus and Mars are shown in grey. Earth's orbit stands out in green between Venus and Mars. As the diagram indicates, the PHAs tend to have more Earth-like orbits than the rest of the NEAs. The asteroid orbits are simulations of what a typical object's path around the sun might look like. The dots in the background are based on data from NASA's NEOWISE, the asteroid-hunting portion of the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission, which scanned the whole sky twice in infrared light before entering hibernation mode in 2011. The blue and orange dots represent a simulation of the population of near-Earth asteroids and the PHAs, respectively, which are larger than 330 feet (100 meters). NEOWISE has provided the best overall look at the PHA population yet, refining estimates of their numbers, sizes, types of orbits and potential hazards. The NEOWISE team estimates that about 20 to 30 percent of the PHAs thought to exist have actually been discovered to date.
Credit:
Album / Science Source / NASA/JPL-Caltech
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
Not available
Print size:
Not available
Keywords:
ART • ARTIST • ARTISTE • ASTEROID • ASTEROIDS • ASTRONOMY • BODY • BV1294 • CELESTIAL • CONCEPT • DISCOVERER • EARTH • EXPLORER • HAZARDOUS • HEAVENLY • ILLUSTRATION • ILLUSTRATIONS • INFRARED • MINOR • MISSION • NEAR • NEAR-EARTH • NEOWISE • OBJECT • OBJECTS • OUTERSPACE • PHA'S • PHA • PLANET • PLANETOID • POTENTIALLY • PROTO-PLANET • PROTOPLANET • RESEARCHER (MALE) • RESEARCHER • SMALL • SOLAR • SPACE (COSMOS) • SPACE • SPATIAL • SURVEY • SYSTEM • TINY • UMBRELLA • WIDE-FIELD
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email

