alb3789801
Alzheimer's Disease, Neurofibrillary Tangles
|
Add to another lightbox |
|
Add to another lightbox |



Buy this image.
Select the use:

Title:
Alzheimer's Disease, Neurofibrillary Tangles
Caption:
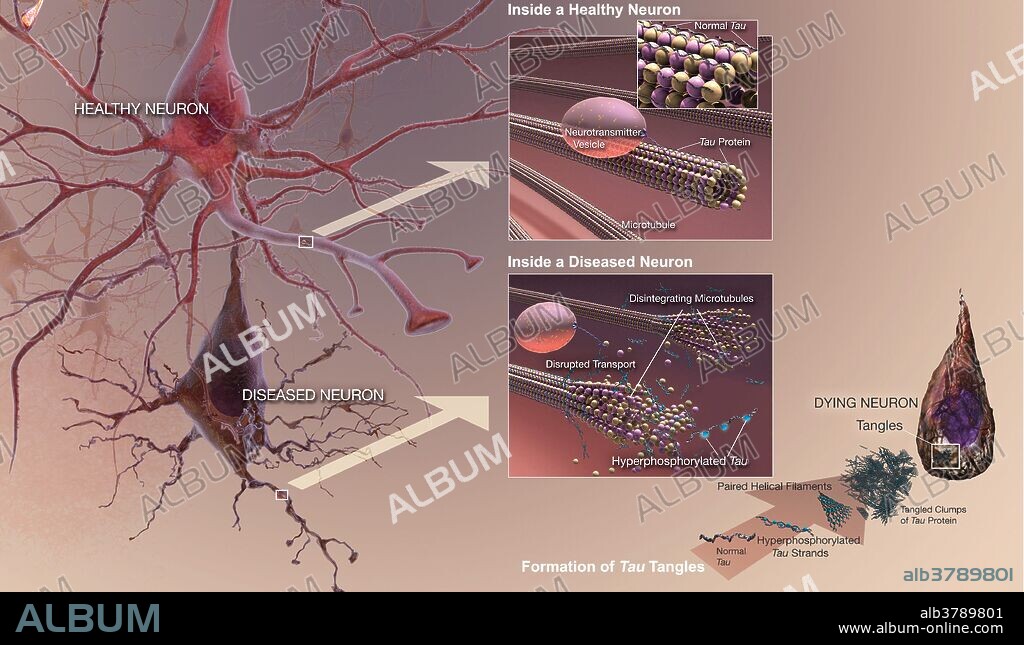
Neurofibrillary Tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary marker of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease (AD), also known as Alzheimer disease, or just Alzheimer's, accounts for 60% to 70% of cases of dementia. It is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and gets worse over time. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events (short-term memory loss). As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self care, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. About 70% of the risk is believed to be genetic with many genes usually involved.
Credit:
Album / Science Source / National Institute on Aging/NIH
Releases:
Model: No - Property: No
Rights questions?
Rights questions?
Image size:
4928 x 2850 px | 40.2 MB
Print size:
41.7 x 24.1 cm | 16.4 x 9.5 in (300 dpi)
Keywords:
21ST CENTURY • 21ST • 21TH CENTURY • AD • ALZHEIMER DISEASE • ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE • ALZHEIMER'S • ALZHEIMERS DISEASE • ALZHEIMERS • ART • ARTIST CONCEPT • ARTWORK • CHRONIC NEURO-DEGENERATIVE DISEASE • CHRONIC NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE • COMPUTER GRAPHIC • CONCEPT • CONCEPTUAL ART • CONCEPTUAL • DAMAGED • DEMENTIA • DISEASE • DISEASED • DISINTEGRATING • DISORDER • DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM • DRAWING • FORMATION • GRAPHIC • HEALTHY • ILLUSTRATION • ILLUSTRATIONS • INFO-GRAPHIC • INFOGRAPHIC • MESS • MESSY • MICROTUBULES • NEURO-DEGENERATIVE • NEURODEGENERATIVE • NEUROLOGIA • NEUROLOGIC • NEUROLOGICAL • NEUROLOGY • NEURON • NEUROTRANSMITTER VESICLE • SCIENCE • SYNAPTIC VESICLE • TAU PROTEIN • TAU TANGLES • TAU • UNHEALTHY
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copy link
Copy link Email
Email
