alb3789851
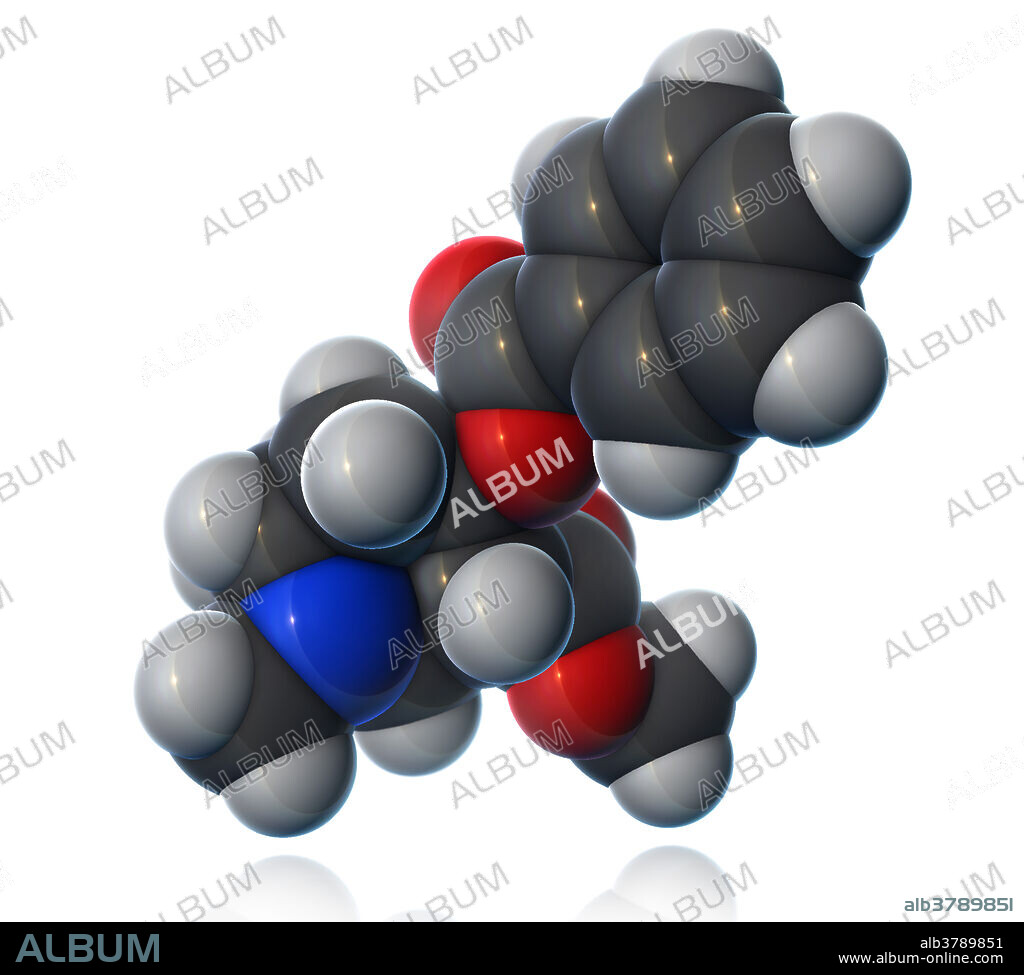
Cocaine Molecular Model, illustration
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen

Título:
Cocaine Molecular Model, illustration
Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
A molecular model of cocaine (C17H21NO4), a stimulant and appetite suppressant drug, obtained from coca plant leaves, which produces low doses of anaesthesia. Cocaine's properties allow it to pass through the blood-brain barrier more easily than other psychoactive chemicals. The drug's addictive nature makes more dangerous than other stimulants, as higher doses can lead to sudden cardiac death. Atoms are coloured dark gray (carbon), light gray (hydrogen), red (oxygen), and blue (nitrogen).
Crédito:
Album / Science Source / Evan Oto
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
6000 x 5400 px | 92.7 MB
Tamaño impresión:
50.8 x 45.7 cm | 20.0 x 18.0 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
ADICCION • ADICTIVO • BOLA • COCAINA • DEPENDENCIA • ESTIMULANTE • ESTRUCTURA • ILUSTRACION • MODEL • MOLECULAR • NARCOTICO • PALO • PSICOACTIVAS • QUIMICA
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
