alb3786765
Riluzole action, Illustration
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen

Título:
Riluzole action, Illustration
Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
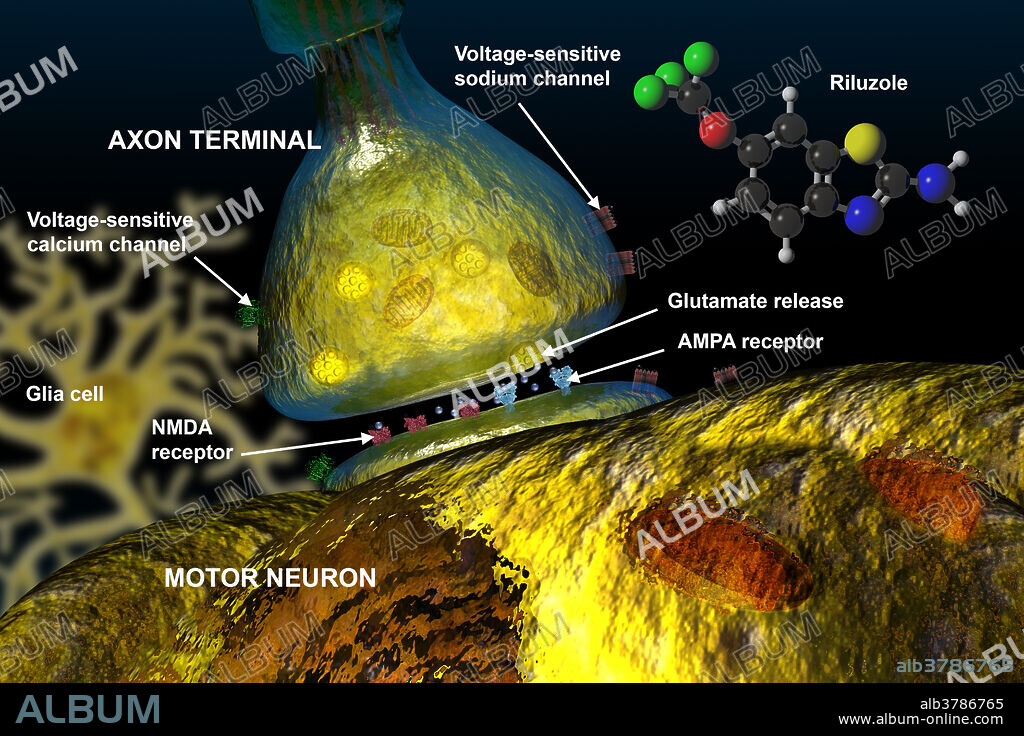
Illustration of the action of riluzole. Riluzole is a neuroprotective drug that blocks the action of the neurotransmitter glutamate in the central nervous system. It inhibits the release of glutamic acid from neurons also blocks some of the postsynaptic effects of glutamic acid by blocking N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. This drug is used to slow the progress of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease). Labelled are axon terminal (large bell shape), sodium channel (reddish squares), glutamate release (bottom of axon), AMPA receptor (blue under axon), NMDA receptor (red under axon), glia cell (faint yellow on left), voltage-sensitive calcium channel (green), and large motor neuron at bottom. The molecular model of riluzole is shown on the right: Black=carbon, white=hydrogen, red=oxygen, blue=nitrogen, green=fluorine, yellow=sulfur.
Crédito:
Album / Science Source / Carol and Mike Werner
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
6060 x 4040 px | 70.0 MB
Tamaño impresión:
51.3 x 34.2 cm | 20.2 x 13.5 in (300 dpi)
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
