alb3816065
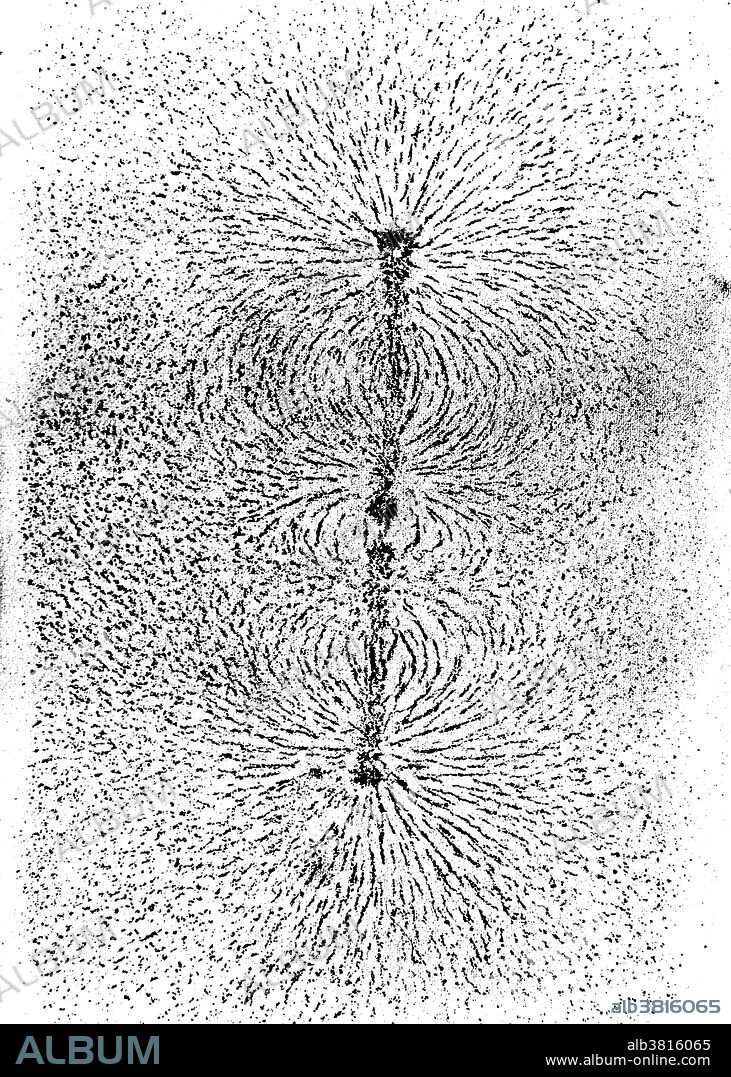
Faraday's Iron Filings Experiment, 1850s
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen.
Selecciona el uso:

Título:
Faraday's Iron Filings Experiment, 1850s
Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
Results of Michael Faraday's iron filings experiment to study magnetic fields generated by magnets, c. 1850s. Michael Faraday (1791-1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Faraday experimented with electricity and magnetism, proposing that magnetism was a circular force. He is also known for discovering magnetic optical rotation, electromagnetic induction, inventing the dynamo, perfecting the Bunsen burner, and formulating the second law of electrolysis. Author of "Chemical Manipulation", Faraday was self-trained and contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry after an apprenticeship in Sir Humphrey Davy's lab. The farad (F) is named after him. As a chemist, Faraday discovered benzene, investigated the clathrate hydrate of chlorine, invented an early form of the Bunsen burner and the system of oxidation numbers, and popularized terminology such as anode, cathode, electrode, and ion.
Crédito:
Album / Science Source / Wellcome Images
Autorizaciones:
Tamaño imagen:
2788 x 3908 px | 31.2 MB
Tamaño impresión:
23.6 x 33.1 cm | 9.3 x 13.0 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
1800S • BLANCO Y NEGRO • BRITANICO • CAMPO MAGNETICO • CIENCIA • ELECTROMAGNETISMO • EXPERIMENTO • FARADAY • FÍSICA (CIENCIA) • HISTORIA • HISTORICO • IMAN • INGLES • MAGNETISMO • QUIMICA • RESULTADOS • SIGLO XIX
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
