alb3810935
Jules Janssen, French Astronomer and Chronophotographer
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen.
Selecciona el uso:

Título:
Jules Janssen, French Astronomer and Chronophotographer
Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
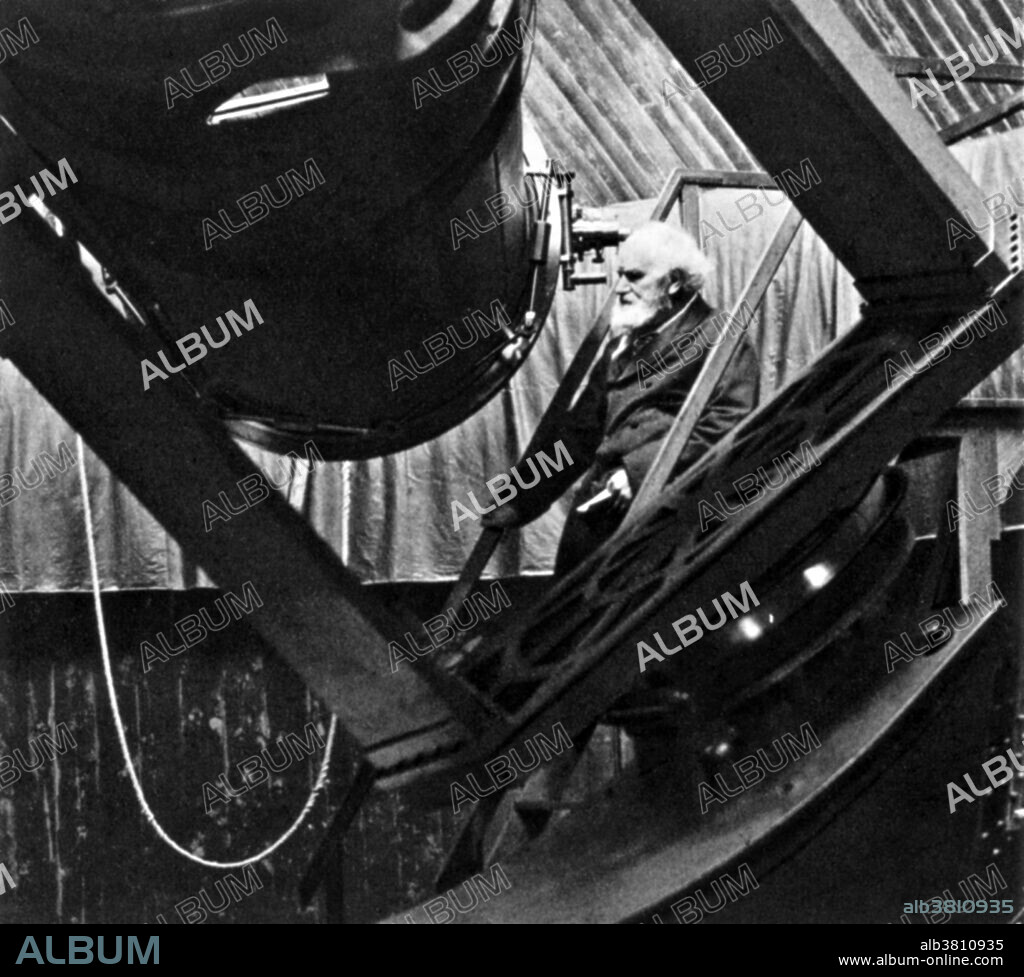
French astronomer, Jules Janssen, poses with his telescope in the late nineteenth century. In this period photography and spectroscopy began to extend the power of telescopic observation. Janssen's photographs of the sun were famous were famous. Pierre Jules Cesar Janssen (1824-1907) was a French astronomer who, along with the English scientist Joseph Norman Lockyer, is credited with discovering the gas helium. In 1857 he went to Peru in order to determine the magnetic equator; in 1861-1862 and 1864, he studied telluric absorption in the solar spectrum in Italy and Switzerland; in 1867 he carried out optical and magnetic experiments at the Azores; he successfully observed both transits of Venus, that of 1874 in Japan, that of 1882 at Oran in Algeria; and he took part in a long series of solar eclipse-expeditions, e.g. to Trani (1867), Guntur (1868), Algiers (1870), Siam (1875), the Caroline Islands (1883), and to Alcosebre in Spain (1905). He was active in the establishment of the astrophysical observatory of Meudon in Paris and in 1876 became its director. There he gathered an important series of solar photographs included in his Atlas de photographies solaires (1904). He later became director of the observatory on Mont Blanc.
Crédito:
Album / Science Source / New York Public Library
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
3549 x 3201 px | 32.5 MB
Tamaño impresión:
30.0 x 27.1 cm | 11.8 x 10.7 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
1907 • ASTRONOMIA • ASTRONOMO • BLANCO Y NEGRO • CIENCIA • CRONOFOTOGRAFÍA • DESCUBRIR • EUROPEA • EUROPEAS • EUROPEO • EUROPEOS • FAMOSA • FAMOSO • FIGURA • FOTO • FOTOGRAFIA • FRANCES • GAS • GENTE • HÉLIO • HISTORIA • HISTORICO • HOMBRE • HOMBRES • IMPORTANTE • MASCULINO • OBSERVATORIO ASTROFISICO • OBSERVATORIO • PARIS • PERSONA • PERSONALIDAD • PERSONALIDADES • PIERRE JULES CESAR JANSSEN • PLANETARIO • PLANETARIOS • RETRATO DE HOMBRE • S. XX • SIGLO XIX • SIGLO XX
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
