alb3801363
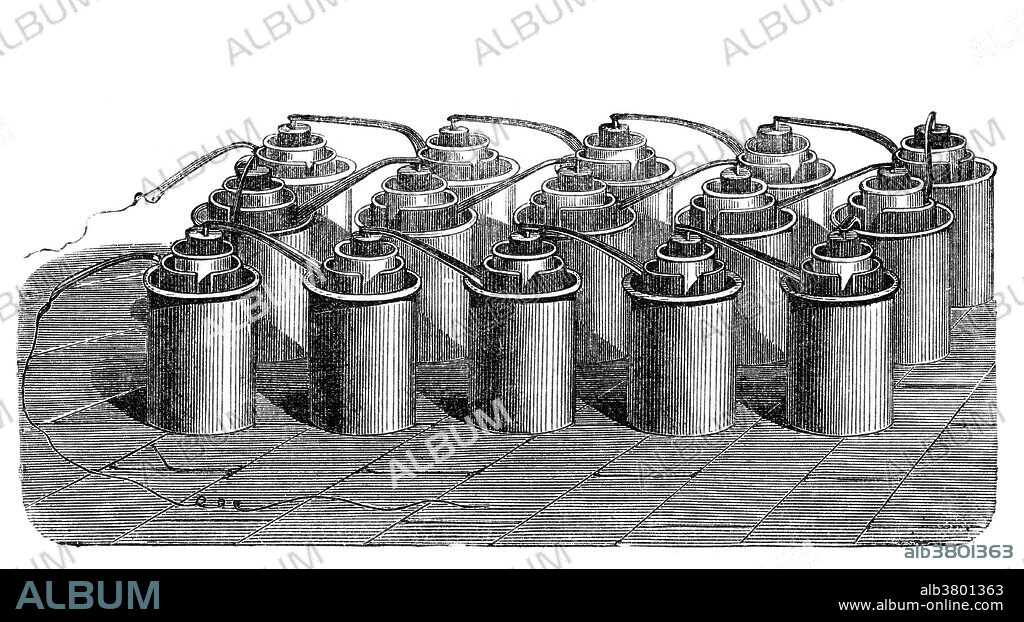
Bunsen Cell Battery, 19th Century
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen.
Selecciona el uso:

Título:
Bunsen Cell Battery, 19th Century
Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
The Bunsen cell battery is a zinc-carbon primary cell composed of a zinc anode in dilute sulfuric acid separated by a porous pot from a carbon cathode in nitric or chromic acid. The cell is named after its inventor, German chemist Robert Wilhelm Bunsen, who improved upon the Grove cell by replacing Grove's expensive platinum cathode with carbon in the form of pulverized coal and coke. Like Grove's battery, Bunsen's emitted noxious fumes of nitrogen dioxide. Bunsen used this cell to extract metals. Henri Moissan used a stack of 90 cells for the electrolysis of hydrogen fluoride to obtain fluorine for the first time.
Crédito:
Album / Science Source
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
4800 x 2665 px | 36.6 MB
Tamaño impresión:
40.6 x 22.6 cm | 16.0 x 8.9 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
ARTE • BLANCO Y NEGRO • BUNSEN • CIENCIA • DE LA BATERÍA • DIBUJO • ELECTRICIDAD • FAMOSA • FAMOSO • FÍSICA (CIENCIA) • GRABADO • HISTORIA • HISTORICO • ILUSTRACION • IMPORTANTE • INVENCION • OBRA DE ARTE • SIGLO XIX
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
