alb8352133
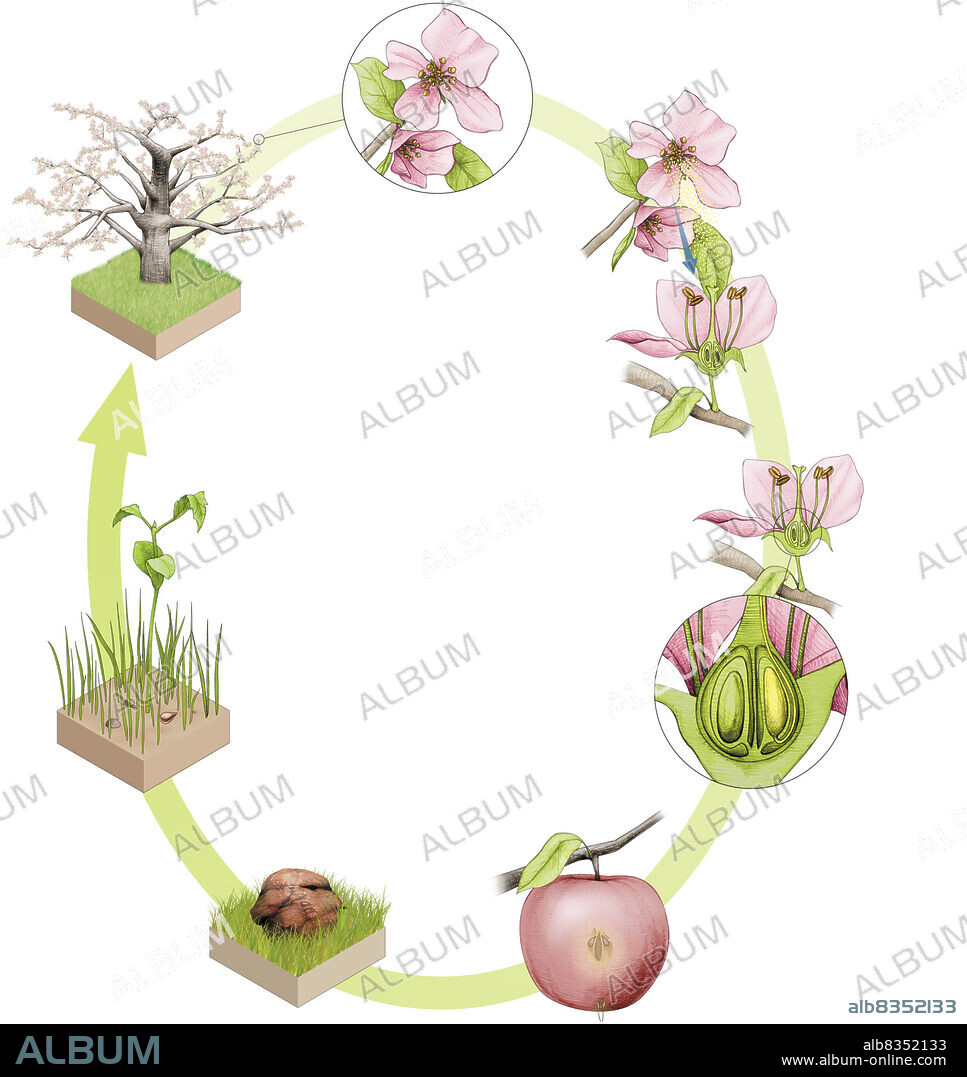
The reproductive cycle of flowering plants can be broken down into six main steps. Flowers contain the plants reproductive organs, which produce pollen grains and ovules. During pollination, the pollen grains are transported, by the wind or a pollinating insect, from a stamen to the tip of a pistil, the organ above the ovaries. The pollen grain germinates in the pistil: it forms a pollen tube that extends down the pistil, enters the ovary, and fertilizes the ovule. The fertilized ovule forms a seed. When the ovary matures, it forms a fruit in which the seeds are enclosed. The fruit detaches itself from the mother plant, opens, and disseminates the seeds that it contains. Germination of a seed gives rise to a seedling, which develops into a plant.
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |
|
Añadir a otro lightbox |



¿Ya tienes cuenta? Iniciar sesión
¿No tienes cuenta? Regístrate
Compra esta imagen.
Selecciona el uso:

Descripción:
Ver traducción automática
The reproductive cycle of flowering plants can be broken down into six main steps. Flowers contain the plants reproductive organs, which produce pollen grains and ovules. During pollination, the pollen grains are transported, by the wind or a pollinating insect, from a stamen to the tip of a pistil, the organ above the ovaries. The pollen grain germinates in the pistil: it forms a pollen tube that extends down the pistil, enters the ovary, and fertilizes the ovule. The fertilized ovule forms a seed. When the ovary matures, it forms a fruit in which the seeds are enclosed. The fruit detaches itself from the mother plant, opens, and disseminates the seeds that it contains. Germination of a seed gives rise to a seedling, which develops into a plant.
Crédito:
Album / Universal Images Group
Autorizaciones:
Modelo: No - Propiedad: No
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
¿Preguntas relacionadas con los derechos?
Tamaño imagen:
2266 x 2400 px | 15.6 MB
Tamaño impresión:
19.2 x 20.3 cm | 7.6 x 8.0 in (300 dpi)
Palabras clave:
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copiar enlace
Copiar enlace Email
Email
