alb9203853
SN 1572, Tycho's Supernova, Arc Explained
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |



Avez-vous déjà un compte? S'identifier
Vous n'avez pas de compte ? S'inscrire
Acheter cette image.
Sélectionnez l'usage:

Titre:
SN 1572, Tycho's Supernova, Arc Explained
Légende:
Voir la traduction automatique
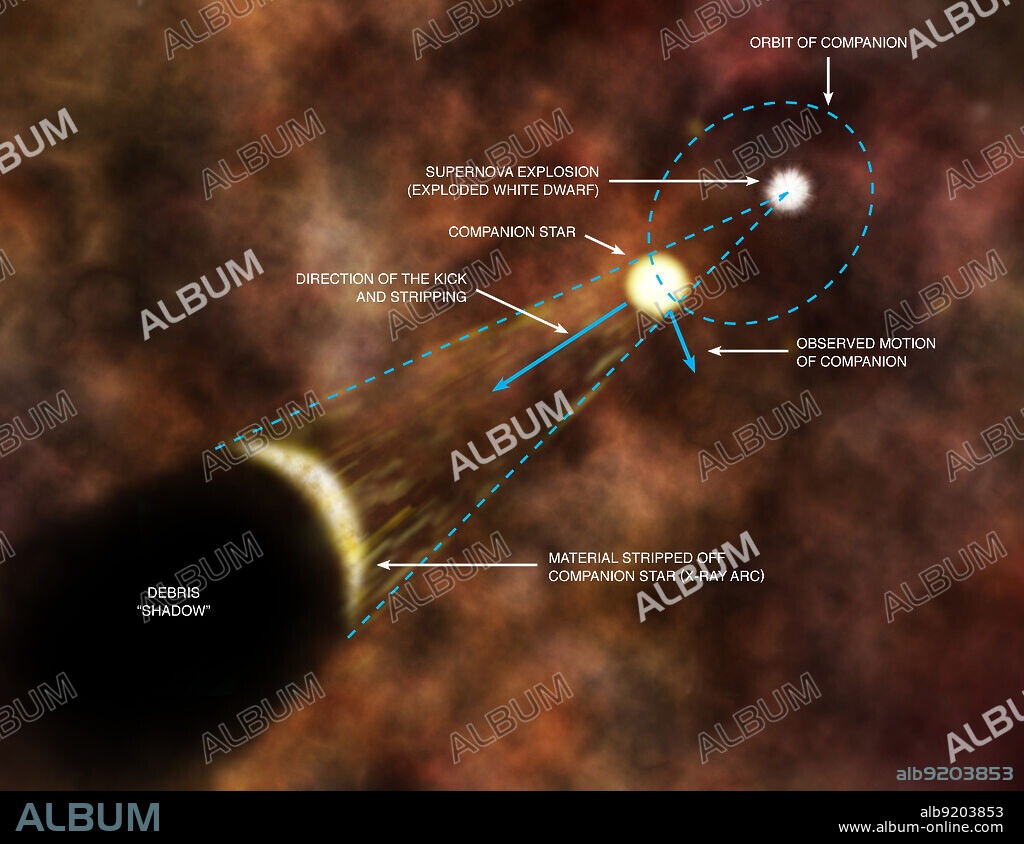
This is an artist's impression showing an explanation from scientists for the origin of an X-ray arc in Tycho's supernova remnant. It is believed that material was stripped off the companion star by the explosion of the white dwarf in the Type Ia supernova explosion, forming the shock wave seen in the arc. The arc has blocked debris from the explosion, creating a "shadow" behind the arc. The force of the explosion imparted a kick to the companion star, and this combined with the orbital velocity of the companion before the explosion to give the observed motion of the companion. Previously, studies with optical telescopes have revealed a star within the remnant that is moving much more quickly than its neighbors, showing that it could be the companion to the supernova. The size of the companion's orbit is not shown to scale here: the separation between it and the white dwarf before the explosion is estimated to have only been about a millionth of a light year, while the full scale of the illustration is over 10 light years.
Crédit:
Album / NASA/CXC/M.Weiss / Science Source
Autorisations:
Modèle: Non - Propriété: Non
Questions sur les droits?
Questions sur les droits?
Taille de l'image:
Pas disponible
Taille d'impression:
Pas disponible
Mots clés:
21E SIECLE • ARTISTE • ARTISTEL • ARTSTE • ASTRONOMIE • CIEL • COSMOS • DETONATION • DIAGRAMME • EXPLOSION • ILLUSTRATION • SCIENCE: ASTRONOMIE • XXIE SIECLE
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copier le lien
Copier le lien Email
Email
