alb3798168
Mitosis, Prophase, LM
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |



Avez-vous déjà un compte? S'identifier
Vous n'avez pas de compte ? S'inscrire
Acheter cette image

Titre:
Mitosis, Prophase, LM
Légende:
Voir la traduction automatique
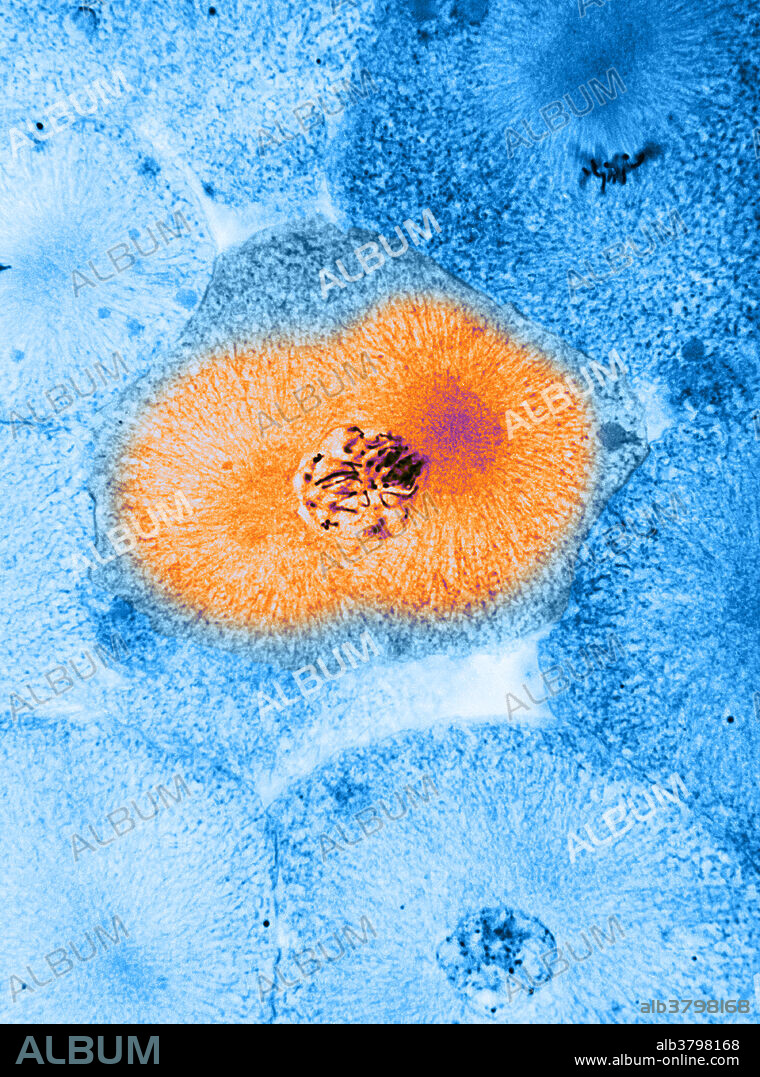
Colour enhanced light micrograph showing mitosis - prophase, in whitefish blastula, the centriole has divided and the daughter centrioles have moved to opposite poles of the cell, a centriole plus the spindle fibers. Magnification 1,100x. Mitosis, the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Blastula, an animal embryo at the stage immediately following the division of the fertilized egg cell, consisting of a ball-shaped layer of cells around a fluid-filled cavity known as a blastocoel. A centriole is a small, cylindrical cell organelle, seen near the nucleus in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic
Crédit:
Album / Science Source / BIOPHOTO ASSOCIATES
Autorisations:
Modèle: Non - Propriété: Non
Questions sur les droits?
Questions sur les droits?
Taille de l'image:
3601 x 4851 px | 50.0 MB
Taille d'impression:
30.5 x 41.1 cm | 12.0 x 16.2 in (300 dpi)
Mots clés:
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copier le lien
Copier le lien Email
Email
