alb3784901
Celiac Disease, Intestinal Villi
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |
|
Ajouter à une autre Lightbox |



Avez-vous déjà un compte? S'identifier
Vous n'avez pas de compte ? S'inscrire
Acheter cette image.
Sélectionnez l'usage:

Titre:
Celiac Disease, Intestinal Villi
Légende:
Voir la traduction automatique
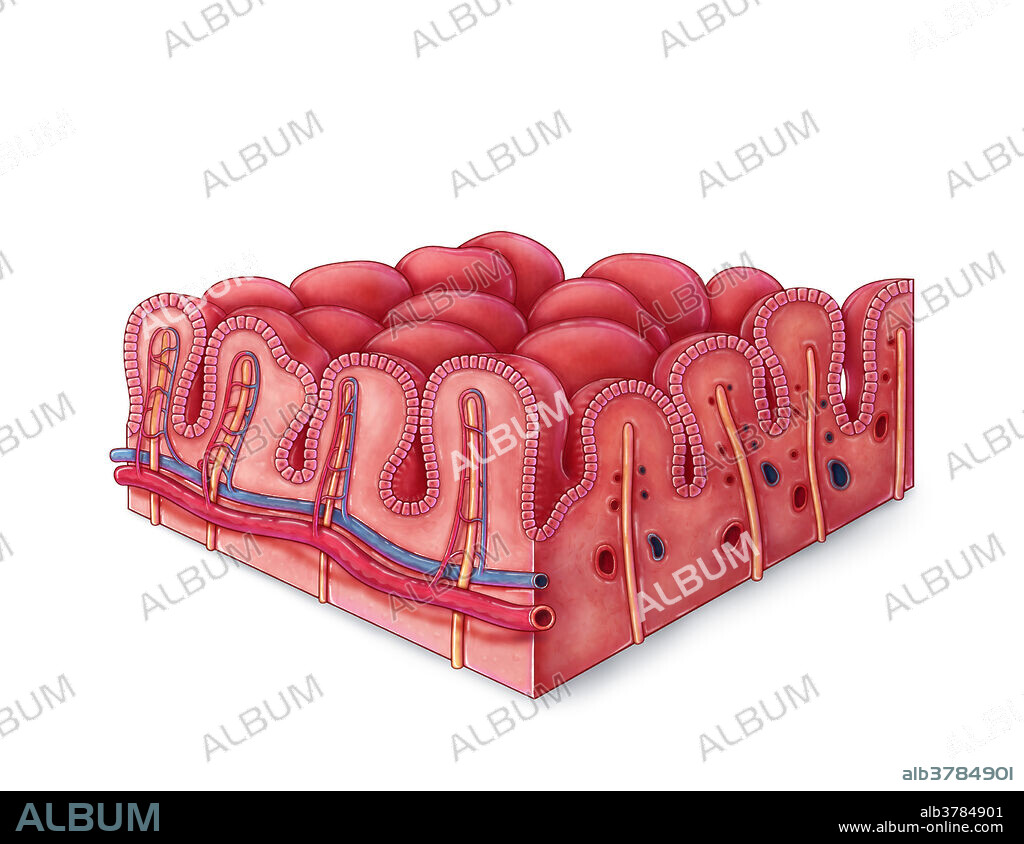
An illustrated section of villi of the small intestine affected by celiac disease. Intestinal villi are finger-like projections extending into the lumen of the small intestine, increasing surface area and aiding nutrient absorption. Capillaries and lacteals (lymph vessels) extend into each villus to collect broken down sugars, amino acids, and fats that diffuse through the epithelium. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder caused by the body's reaction to a protein found in wheat and grains, known as gluten. When celiac patients consume gluten, the immune system releases antibodies and creates an inflammatory response, resulting in symptoms like diarrhoea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and other gastrointestinal problems. Inflammation and damage caused by the immune response can result in blunting of the intestinal villi, hindering absorption and often leading to complications like anaemia or malnutrition.
Crédit:
Album / Science Source / Evan Oto
Autorisations:
Taille de l'image:
3300 x 2550 px | 24.1 MB
Taille d'impression:
27.9 x 21.6 cm | 11.0 x 8.5 in (300 dpi)
 Pinterest
Pinterest Twitter
Twitter Facebook
Facebook Copier le lien
Copier le lien Email
Email
